本文的查询是指存储了5个手机数据后再查询。存储实现见文章:【Node.js】mongoose教程–存储。
GitHub源码链接:sodino#MongoDemo
Model与Query
Model.find()方法会返回Query对象。
Model.find()方法原型如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Model.find(conditions, [projection], [options], [callback])
Finds documents
Parameters:
conditions <Object>
[projection] <Object> optional fields to return (http://bit.ly/1HotzBo)
[options] <Object> optional
[callback] <Function>
Returns:
<Query>
|
参数conditions是必填项,用于设定查询条件。
参数projection是可选项,用于设定查询结果的返回对象所包含的字段范围。例如查询的Phone返回的结果对象只包含device字段或去除device字段。详情见链接$project (aggregation)。
参数options是可选项,用于对查询的结果做功能处理,如排序sort、数量限制limit、查询跳跃skip等功能。详情见链接Query.Options.
参数callback是可选项,用于获取查询结果。
该方法执行后,返回Query一个对象。
Query可以提供更加简洁明了的查询方法,这些查询方法都与Model.find()中的参数conditions、projection、options几乎存在着一一对应的功能关系。
如where() or() gte()与conditions、select()与projection、sort() limit()与options。
Query也有一些功能扩展函数,如计算count()、排重distinct();也可以直接用于更新与删除数据。
Query推荐使用链式调用的代码编写方式,在链式代码的末尾调用.exec(callback)获取查询结果。
如以下代码演示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| // 查询:价格大于等于1000且小于等于4000,
// 且设备名称包含大小写不敏感的`huawei`,
// 并获取该手机安装的的前2个app
// chaining
Phone
.where('price').gte(1000).lte(4000)
.where('device', /^huawei/i)
.where('apps').slice(2)
.exec(callback)
|
下面来演示一些查询的示例:
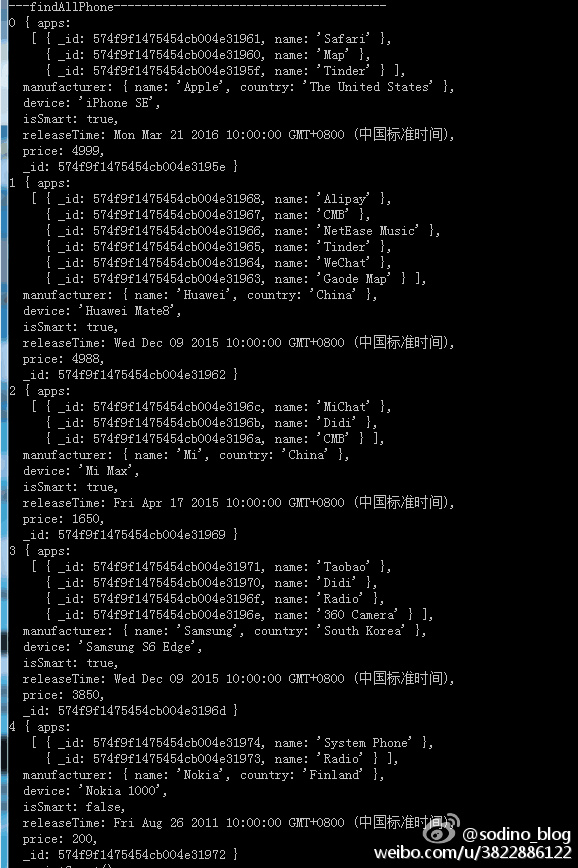
查询全部数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| Phone.find((err, phones) => {
if (err) {
console.log('findAllPhone err:', err);
} else {
console.log('---findAllPhone---------------------------------------');
phones.forEach((element, index, phones) => {
console.log(index, element);
});
}
|
控制台输出:
条件查询
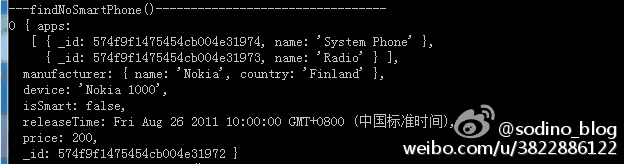
找出非智能手机:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function findNoSmartPhone() {
Phone.find({isSmart : false}).exec((err, phones) => {
console.log('---findNoSmartPhone()---------------------------------');
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
phones.forEach((element, index, phones) => {
console.log(index, element);
});
}
});
}
|
控制台输出:
条件查询–数组
在Phone中,有个apps中为包含一个name字段的对象数组。定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| // 开始定义Schema
var phoneSchema = new Schema({
... ...
apps : [{name : String}],
... ...
});
|
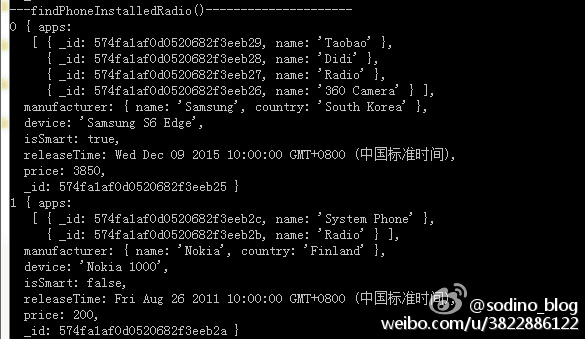
如果需要查找安装了哪些手机安装了Radio这个软件,编写条件为{"apps.name" : "Radio"}可以这么查询:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function findPhoneInstalledRadio() {
Phone.find({'apps.name' : 'Radio'}).exec((err, phones)=>{
console.log('---findPhoneInstalledRadio()---------------------');
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
phones.forEach((element, index, phones) => {
console.log(index, element);
})
}
});
}
|
控制台输出如下:
组合条件查询
在上面的两个查询演示了普通字段及数组下对象字段的指定条件查询,但都是单条件查询。
现在演示更加复杂的组合条件查询。
即涉及到对比条件或逻辑条件的拼装。
对比条件操作符(点击查看详情):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| $eq // 相等
$ne // 不等于
$gt // 大于
$gte // 大于等于
$lt // 小于
$lte // 小于等于
$in // 属于,处于
$nin // 不属于,不处于
|
逻辑条件操作符(点击查看详情):
1
2
3
4
| $or // 或
$and // 且
$not // 非
$nor // 对$or的条件取反,即$or的补集
|
以上的操作符可用直接用在Model.find()中的conditions参数中;当然Query类也提供了一一对应的查询方法。
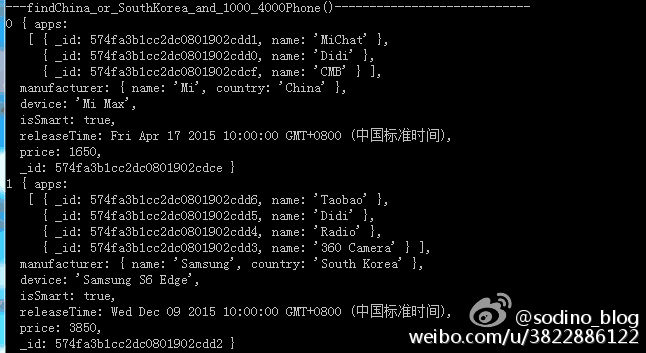
以下代码演示组合条件:* 查找中国或韩国厂商且价格处于[1000, 4000)范围内的手机 *
可以有如下4种查询方式,它们的查询结果是等价的。
方法1和方法3在Model.find()中condictions参数直接使用运算操作符;
方法2和方法4使用Query.where().[chain_methods()].exec(callback)方式。
两种方法是等价的,爱用哪个用哪个吧。
在本例子中,可以发现$or和$in在某些场合是可以等价转换的。
即以下两种方式表达的意思都是指手机厂商是China或South Korea:
1
2
3
4
| $or:[
{'manufacturer.country':'China'},
{'manufacturer.country':'South Korea'}
]
|
1
2
3
4
| {
'manufacturer.country' :
{$in:['China', 'South Korea']}
}
|
接下来看4种方法的代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| // 方法1
Phone.find({$or:[
{'manufacturer.country':'China'},
{'manufacturer.country':'South Korea'}
], $and:[
{'price' : {$gte : 1000}},
{'price' : {$lt : 4000}}
]
}).exec((err, phones) => {
console.log('---findChina_or_SouthKorea_and_1000_4000Phone()----------------------------');
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
phones.forEach((element, index, phones) => {
console.log(index, element);
});
}
});
// 方法2
Phone.find()
.or([{'manufacturer.country':'China'}, {'manufacturer.country':'South Korea'}])
.where('price').gte(1000).lt(4000)
.exec((err, phones) => {
console.log('---findChina_or_SouthKorea_and_1000_4000Phone()----------------------------');
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
phones.forEach((element, index, phones) => {
console.log(index, element);
});
}
});
// 方法3
Phone.find({'manufacturer.country' :
{$in:['China', 'South Korea']},
$and:[
{'price' : {$gte : 1000}},
{'price' : {$lt : 4000}}
]
}).exec((err, phones) => {
console.log('---findChina_or_SouthKorea_and_1000_4000Phone()----------------------------');
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
phones.forEach((element, index, phones) => {
console.log(index, element);
});
}
});
// 方法4
Phone.find()
.where('manufacturer.country').in(['China', 'South Korea'])
.where('price').gte(1000).lt(4000)
.exec((err, phones) => {
console.log('---findChina_or_SouthKorea_and_1000_4000Phone()----------------------------');
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
phones.forEach((element, index, phones) => {
console.log(index, element);
});
}
});
|
控制台输出如下:
下一篇mongoose教程–排序
About Sodino



